Discovering the true implications of medication on elderly individuals is crucial for maintaining their well-being and quality of life.
In today’s fast-paced world, where the pursuit of health and happiness is a prominent concern, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the effects that certain medications can have on older individuals.
Unlocking the secrets of amitriptyline in the elderly population can empower both healthcare professionals and caretakers to make informed decisions and minimize any potential risks.
By delving into the intricate details and exploring alternative treatments, we can pave the way for a healthier, happier, and more fulfilling life for our elderly loved ones.
Understanding the Adverse Reactions of Amitriptyline in Older Adults
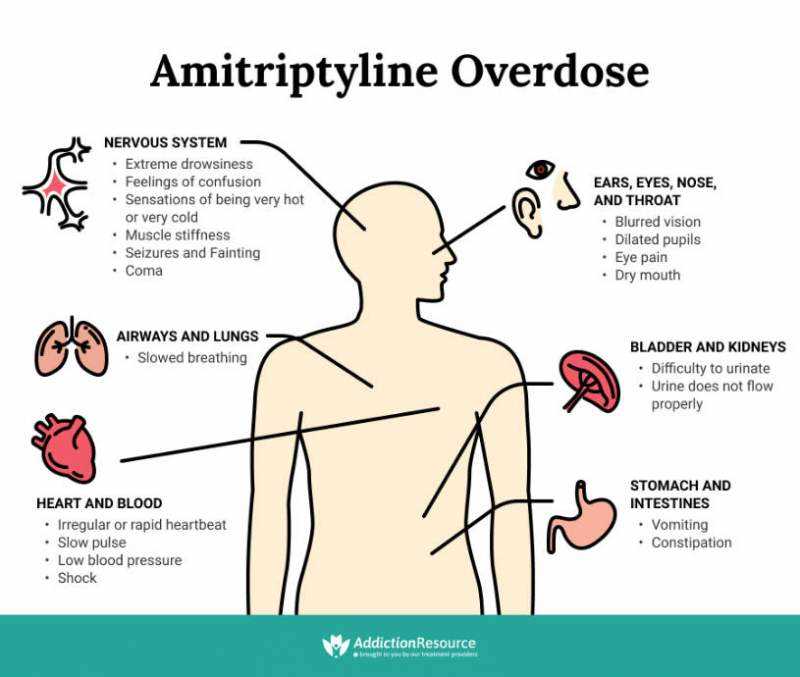
In this section, we will delve into the potential drawbacks that may arise when prescribing amitriptyline to elderly patients. By exploring the adverse reactions associated with this medication, healthcare professionals can make better informed decisions regarding its use in older adults.
| Adverse Reaction | Description |
|---|---|
| Impaired Cognitive Function | Amitriptyline has been known to negatively impact cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance in elderly patients. |
| Orthostatic Hypotension | Elderly individuals taking amitriptyline may experience a drop in blood pressure upon standing up, which can lead to dizziness, lightheadedness, and an increased risk of falls. |
| Weight Gain | Amitriptyline use has been associated with weight gain in older adults, which can lead to various health complications such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. |
| Urinary Retention | Some elderly patients may experience difficulty in emptying their bladder while taking amitriptyline, which can lead to urinary retention and increase the risk of urinary tract infections. |
| Increased Heart Rate | Amitriptyline has the potential to cause an elevated heart rate in older adults, which can be concerning for individuals with existing cardiovascular conditions. |
It is important for healthcare providers to be aware of these potential side effects in order to provide appropriate care and monitoring for elderly patients taking amitriptyline. By closely monitoring patients and managing these adverse reactions, healthcare professionals can help minimize their impact and ensure the well-being of older individuals.
Common Adverse Reactions of Amitriptyline on Elderly Patients
As individuals age, their bodies undergo various physiological changes that can impact the way medications are metabolized and processed. Amitriptyline, a commonly prescribed tricyclic antidepressant, is known to have several potential side effects that may affect elderly patients in particular. It is crucial for healthcare providers and caregivers to be aware of these common adverse reactions to ensure the well-being and safety of elderly patients receiving this medication.
1. Cognitive Impairment
One of the most prevalent adverse reactions experienced by elderly patients taking amitriptyline is cognitive impairment. This includes difficulties with memory, attention, concentration, and thinking processes. While the exact mechanism behind this adverse reaction is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to the medication’s effect on certain neurotransmitters in the brain. Elderly patients may experience a decline in cognitive abilities, which can significantly impact their daily functioning and overall quality of life.
2. Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, or a sudden drop in blood pressure when standing up, is another common side effect of amitriptyline in elderly patients. This adverse reaction can increase the risk of falls and injuries among this population, as dizziness and lightheadedness can occur when transitioning from a sitting or lying position to standing. Healthcare providers should closely monitor blood pressure levels and educate patients on proper techniques to minimize the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
3. Blurred Vision
Amitriptyline can also affect vision in elderly patients, leading to blurred vision and other visual disturbances. These side effects may be dose-dependent and can impact activities such as reading, driving, or performing other tasks that require clear vision. Individuals experiencing blurred vision while taking amitriptyline should report it to their healthcare provider, who may adjust the medication dosage or explore alternative treatment options.
4. Dry Mouth and Constipation
Dry mouth and constipation are two additional common adverse reactions of amitriptyline in elderly patients. Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, occurs due to a reduction in saliva production and can lead to discomfort and difficulty in eating, speaking, and swallowing. Constipation, on the other hand, results from the medication’s impact on intestinal motility and can cause abdominal pain and discomfort. Adequate hydration and dietary fiber intake are recommended to alleviate these side effects.
It is important for healthcare providers and caregivers to monitor elderly patients taking amitriptyline for these common adverse reactions and provide appropriate interventions to manage and minimize their impact. Open communication and regular follow-ups between patients, their caregivers, and healthcare providers are essential to ensure the well-being and safety of elderly individuals taking this medication. Alternative approaches to treating elderly patients should also be considered when necessary to mitigate these potential side effects and improve overall outcomes.
Impact of Amitriptyline on Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may experience various consequences when taking Amitriptyline, a medication commonly prescribed for certain conditions. These consequences can significantly affect their overall well-being and quality of life. It is essential for healthcare providers to understand and manage these impacts to ensure the safety and comfort of elderly patients.
Physical Considerations:
One aspect that needs careful attention is the influence of Amitriptyline on the physical well-being of elderly patients. This medication can lead to changes in bodily functions, such as metabolism, digestion, and cardiovascular health. Healthcare providers must closely monitor these effects and adjust treatment plans accordingly to minimize any negative impacts on their patients.
Psychological Effects:
In addition to physical effects, Amitriptyline can also have a profound impact on the psychological well-being of elderly patients. This medication can alter their cognition, memory, and emotional state. It is crucial for healthcare providers to carefully assess these effects and offer necessary support to mitigate any potential adverse psychological impacts on the patients.
Interactions with Other Medications:
Another critical consideration is the potential interactions between Amitriptyline and other medications elderly patients may be taking. Polypharmacy is common among the elderly, and it is essential to identify any potential conflicts or adverse reactions that may occur when Amitriptyline is combined with other drugs. Healthcare providers should take these interactions into account when prescribing and managing Amitriptyline for their elderly patients.
Managing and Minimizing Impact
To manage and minimize the impact of Amitriptyline on elderly patients, healthcare providers must adopt a multifaceted approach. This includes:
- Educating patients and their caregivers about the potential impacts and how to identify and report any concerning symptoms
- Regular monitoring of patients’ physical and psychological well-being through comprehensive assessments and check-ups
- Collaborating with other healthcare professionals to optimize the overall treatment plan, including modifications to medication dosages or combinations
- Providing support and resources to help patients cope with the potential side effects and maintain their overall quality of life
By implementing these strategies, healthcare providers can effectively manage the impact of Amitriptyline on elderly patients, ensuring their well-being and promoting the best possible outcomes.
Managing and Minimizing Adverse Reactions
As we age, our bodies become more sensitive to certain medications, which can lead to an increased risk of experiencing undesirable effects. When it comes to the treatment of elderly patients, it is crucial to carefully manage and minimize adverse reactions to medication, including the use of amitriptyline.
Understanding and Identifying Adverse Reactions
It is important for healthcare providers to have a thorough understanding of the potential adverse reactions that may occur in elderly patients taking amitriptyline. By being knowledgeable about these reactions, healthcare providers can monitor patients closely and swiftly identify any signs of adverse effects.
Individualized and Weight-Adjusted Dosing
One strategy in managing and minimizing adverse reactions is to prescribe individualized and weight-adjusted doses of amitriptyline for elderly patients. By taking into account an individual’s weight, age, and overall health condition, healthcare providers can ensure that the dosage is tailored to their specific needs, reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
Regular Monitoring and Assessment
Regular monitoring and assessment of elderly patients taking amitriptyline is essential in identifying any potential adverse reactions. This includes regular check-ups, laboratory tests, and physical examinations to closely monitor the patient’s response to the medication and detect any signs of adverse reactions early on.
Supportive Care and Education
Providing elderly patients with comprehensive supportive care and education can play a significant role in managing and minimizing adverse reactions. By educating them about the potential side effects and how to recognize and report any concerning symptoms, patients can actively participate in their treatment process and seek immediate medical attention if necessary.
In conclusion, managing and minimizing adverse reactions in elderly patients taking amitriptyline requires a comprehensive approach that includes understanding and identifying adverse reactions, individualized dosing, regular monitoring and assessment, and supportive care and education. By implementing these strategies, healthcare providers can help elderly patients maximize the benefits of amitriptyline while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Monitoring the Effects of Amitriptyline in Elderly Patients
Ensuring the well-being of elderly patients who are undergoing treatment with Amitriptyline requires careful monitoring of its impact on their overall health and quality of life. This involves observing and documenting any changes or reactions that occur as a result of the medication, and taking appropriate measures to address them.
Observation and Documentation: Healthcare providers need to closely monitor the elderly patients taking Amitriptyline to evaluate its effects on their physical and mental well-being. Symptoms such as drowsiness, confusion, or changes in appetite should be carefully noted and recorded. This detailed documentation can help identify patterns, recognize potential adverse reactions, and guide any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Regular Check-ups: It is crucial to schedule regular check-ups with elderly patients who are on Amitriptyline. These appointments provide an opportunity to assess the drug’s impact, monitor vital signs, and evaluate any changes in symptoms. Regular check-ups also offer an opportunity for patients to share their experiences, ask questions, and voice any concerns they may have.
Collaborative Approach: Monitoring the effects of Amitriptyline in elderly patients requires a collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, caregivers, and the patients themselves. By working together, the healthcare team can gather comprehensive information about the patient’s response to the medication, enabling them to make informed decisions and provide appropriate support.
Continued Evaluation: The monitoring process should not end after the initial stages of treatment. Ongoing evaluation is essential to ensure that the effects of Amitriptyline are effectively managed and that the elderly patients are responding positively. Regular assessments help track progress, identify any new side effects, and determine the need for any modifications in the treatment plan.
Education and Support: It is crucial to educate both the elderly patients and their caregivers about what to expect while taking Amitriptyline. This involves providing information on possible effects, discussing strategies to manage them, and addressing any concerns or misconceptions. Ensuring ongoing support and guidance can help patients and their caregivers feel more confident and engaged in the monitoring process.
In conclusion, monitoring the effects of Amitriptyline in elderly patients is a comprehensive and diligent process. By carefully observing and documenting any changes, scheduling regular check-ups, involving all relevant stakeholders, and providing education and support, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of elderly patients as they undergo this medication.
An Alternative Approach to Treating Elderly Patients
When it comes to the treatment of older individuals, it is important to consider alternative methods that can effectively address their unique needs and circumstances. In the case of managing symptoms and improving overall well-being, exploring alternative approaches can provide new possibilities for elderly patients.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies offer a holistic approach to healthcare, focusing on the individual as a whole rather than solely targeting the symptoms or conditions. These therapies can include acupuncture, massage therapy, mindfulness practices, and herbal remedies. By incorporating these into a comprehensive treatment plan, elderly patients may experience a reduction in discomfort and an improved quality of life.
Diet and Nutrition
The impact of diet and nutrition on overall health and well-being cannot be overstated. For elderly patients, it is important to ensure a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients and vitamins. Consulting with a nutritionist or dietitian can provide valuable insights into creating a meal plan that supports optimal health and complements any medication or treatment being used.
| Nutrient | Sources |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Dairy products, leafy green vegetables |
| Vitamin D | Sunlight, fatty fish, fortified foods |
| Magnesium | Nuts, seeds, whole grains |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts |
By ensuring that elderly patients receive an appropriate intake of essential nutrients, their overall health and well-being can be enhanced, potentially reducing the need for certain medications and minimizing adverse effects.
Ultimately, adopting an alternative approach to treating elderly patients goes beyond simply managing symptoms. It involves considering the person as a whole and addressing their unique needs through complementary therapies and a supportive diet. By doing so, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall well-being and quality of life of elderly individuals.